-
- What are the main security challenges of SD-WAN?
- What are the primary SD-WAN security features?
- What is AI’s role in improving SD-WAN security?
- What is the role of SASE in SD-WAN security?
- Do next-generation SD-WAN solutions provide better security?
- What is the difference between SD-WAN security and secure SD-WAN?
- SD-WAN security FAQs
What Is SD-WAN Security? | SD-WAN Security Considerations
5 min. read
Table of contents
SD-WAN security is the application of protective measures and protocols designed to safeguard the integrity and data within an SD-WAN network.
It often involves the integration of additional security services or devices that enhance the network's defenses against external threats and vulnerabilities. These measures typically include the use of third-party security solutions like cloud-based services or specialized security appliances, which work in conjunction with SD-WAN technology.
What are the main security challenges of SD-WAN?
Inherently, traditional SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) solutions aren’t equipped with integrated security features.
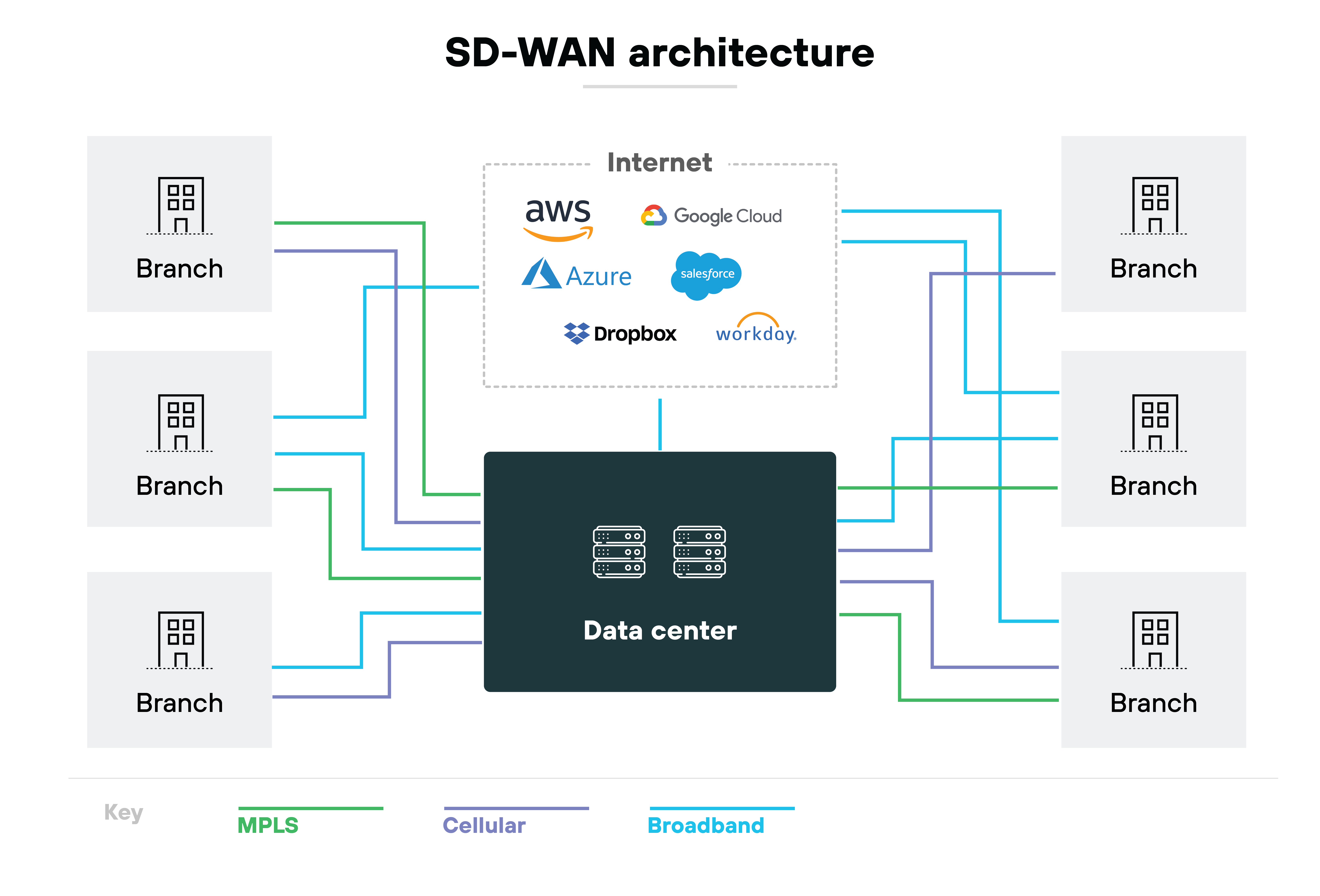
Which means that network security teams sometimes have to route all network traffic through a comprehensive security stack to conduct inspections and implement threat prevention measures.
Consequently, organizations face a dilemma: either forgo the security of WAN traffic or compromise on SD-WAN's advantages by rerouting all traffic back to the data center for thorough checks.
Not to mention, when security features are integrated into SD-WAN solutions, they don’t always offer the sophistication necessary for defending against modern cyber threats.
To effectively secure corporate WANs, organizations need to pair SD-WAN's network optimization capabilities with advanced security capabilities. Later in the article, we’ll talk through some of the ways to do that.
For now, we’ll focus on the security challenges organizations often face when it comes to SD-WAN.
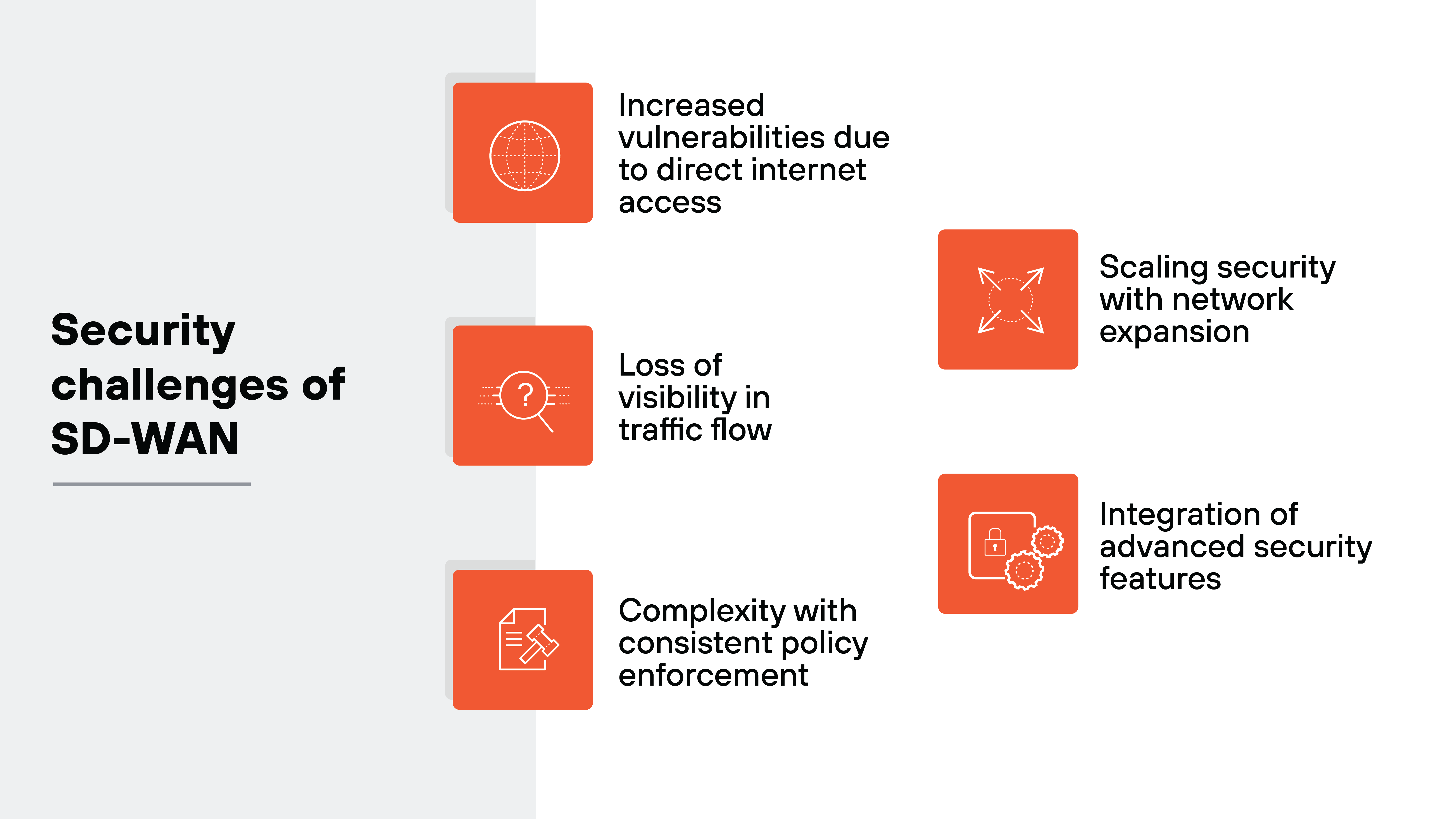
The primary security challenges of SD-WAN generally include:
- Increased vulnerabilities due to direct internet access
- Loss of visibility in traffic flow
- Complexity with consistent policy enforcement
- Scaling security with network expansion
- Integration of advanced security features
Let’s dive into the details.
Further reading: Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: What Are the Differences?
Increased vulnerabilities due to direct internet access
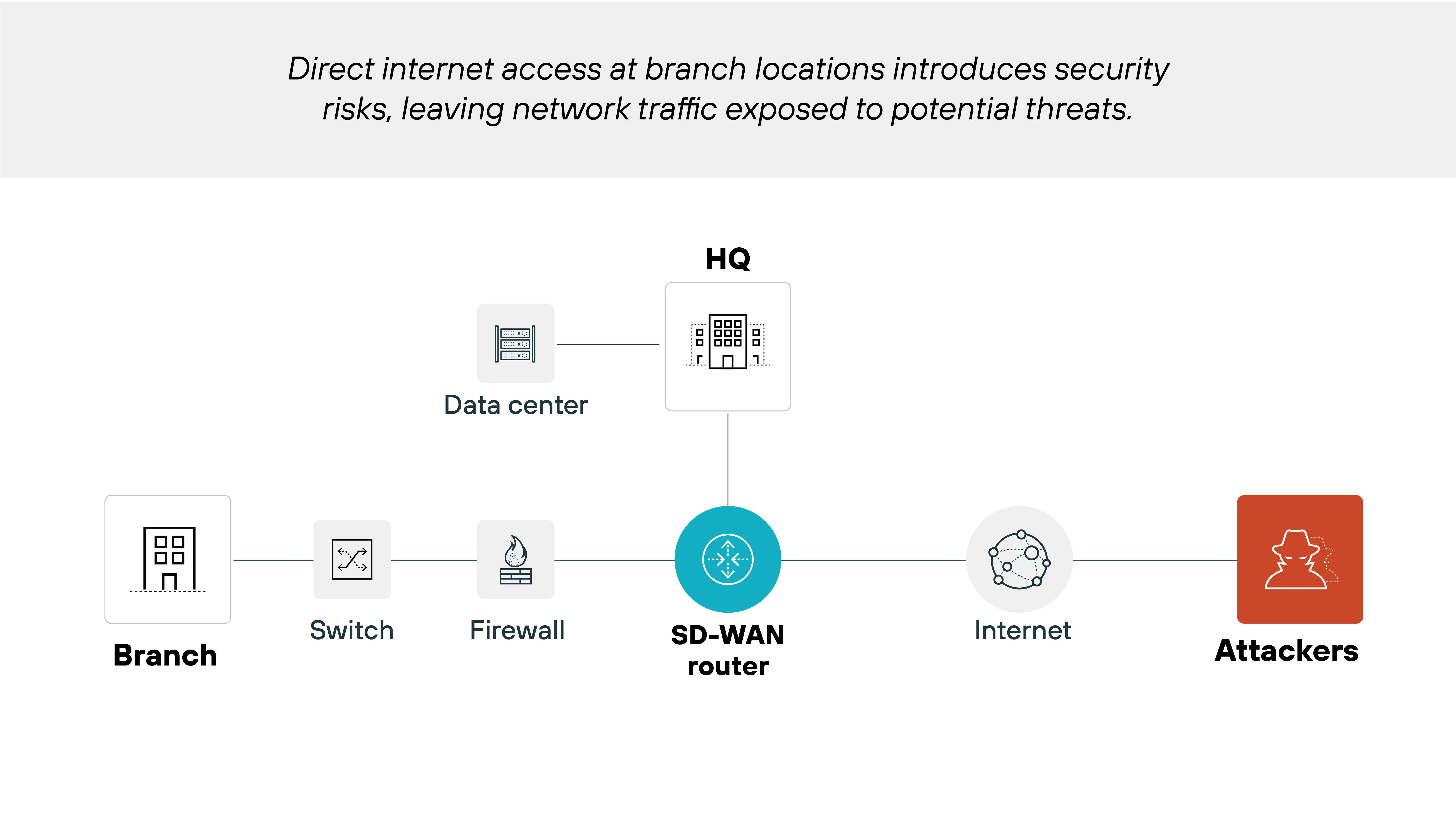
Direct internet access at branch locations can introduce unique security risks.
SD-WAN often relies on direct internet connections that bypass the centralized security controls typically found at a corporate data center. This can leave network traffic more exposed to potential threats and breaches.
This configuration demands strong, localized security measures to protect against vulnerabilities that can be exploited via open connections.
Loss of visibility in traffic flow
Monitoring challenges can sometimes arise with SD-WAN's dynamic routing.
SD-WAN’s ability to route traffic across multiple pathways can complicate the monitoring process, potentially leading to blind spots.
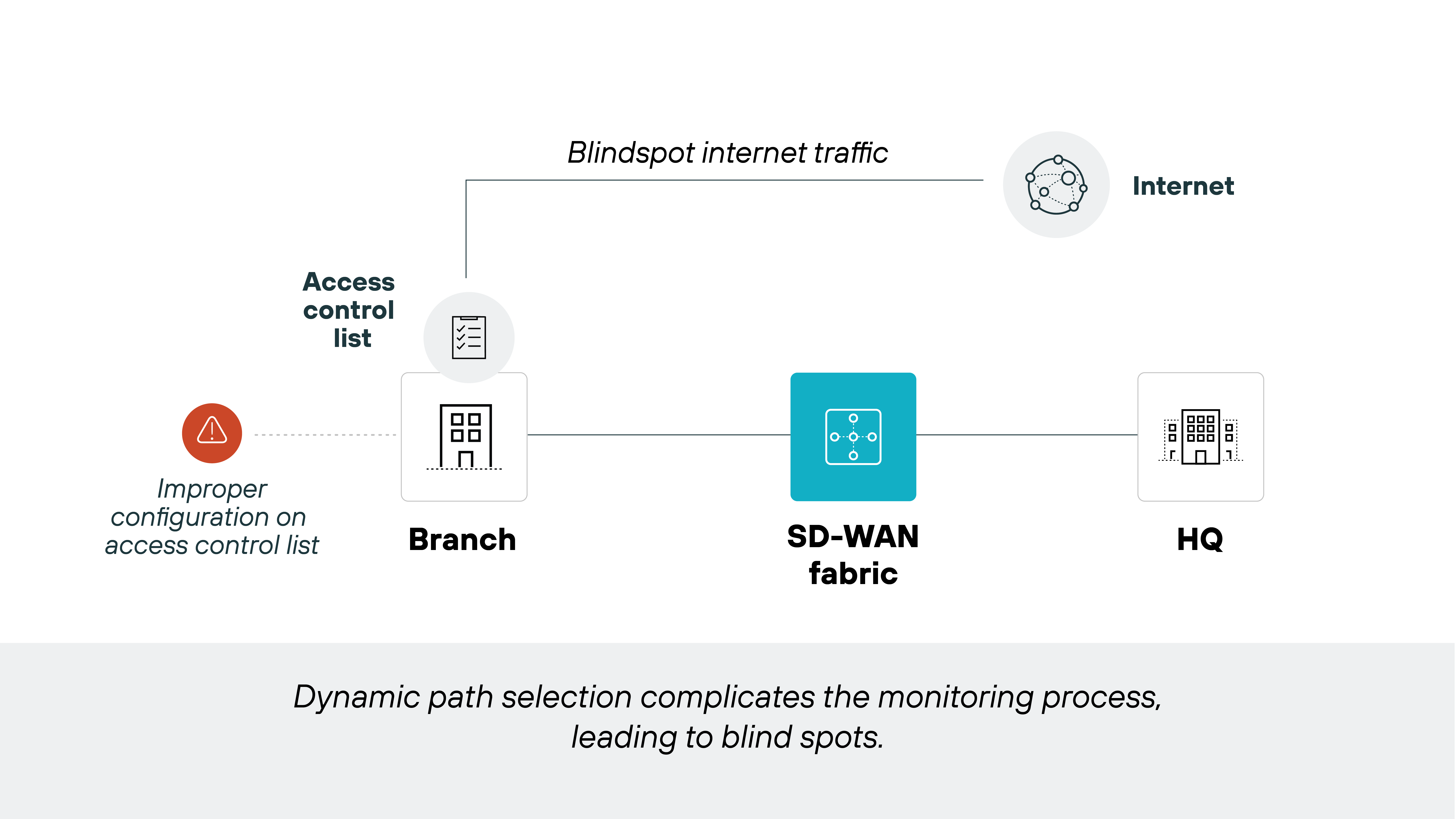
Blind spots are problematic because they can prevent the detection of unauthorized activities and vulnerabilities. Which obviously poses a major risk to network integrity and data security.
Complexity with consistent policy enforcement
Implementing uniform security policies across all locations is more complex with SD-WAN.
Due to varying needs at different organizational sites, consistently applying comprehensive security policies tends to become challenging.
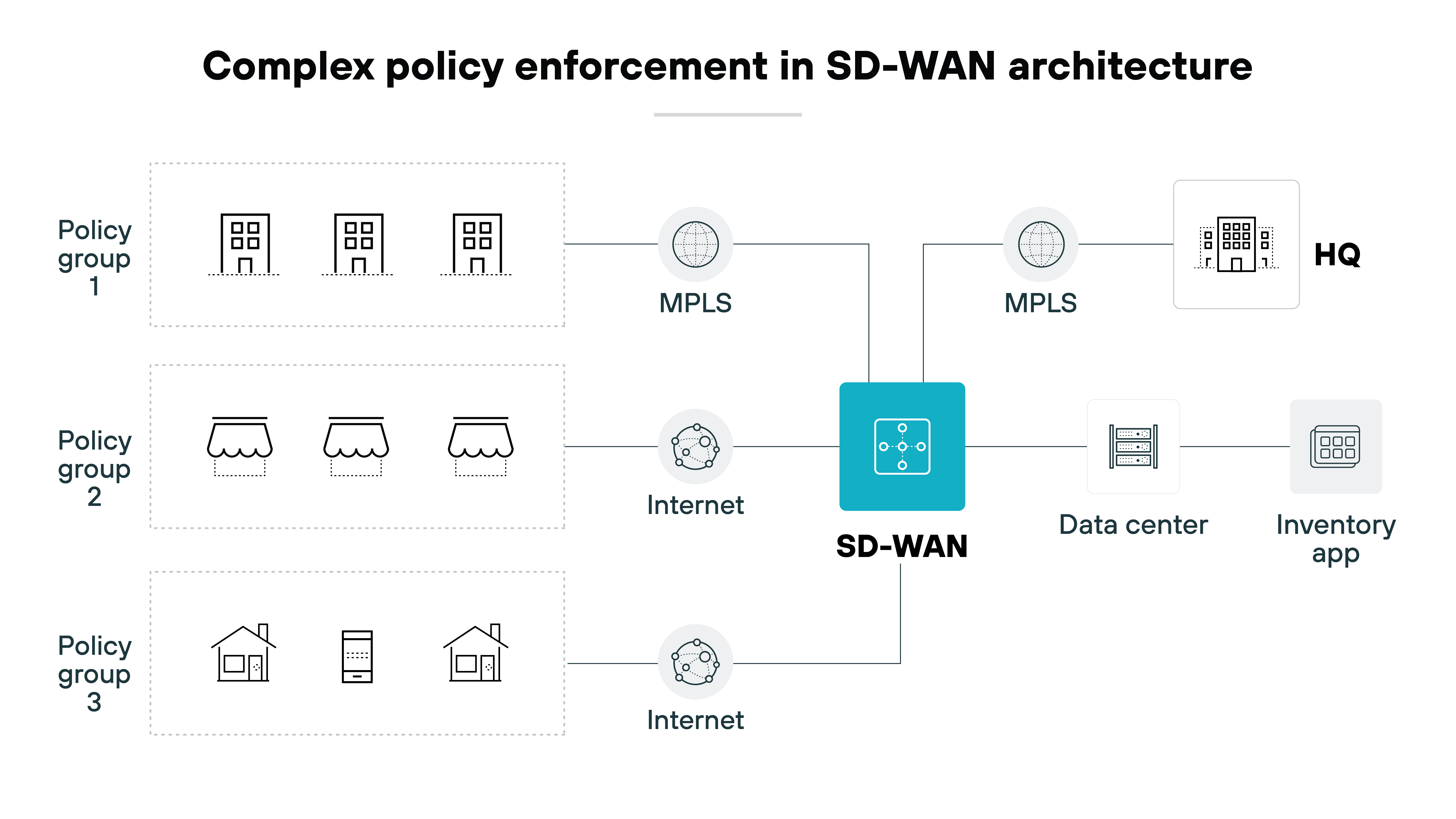
The inconsistency can lead to security lapses, where some areas of the network might be less protected than others—making them targets for cyberattacks.
Scaling security with network expansion
Scalability of security measures is another big challenge.
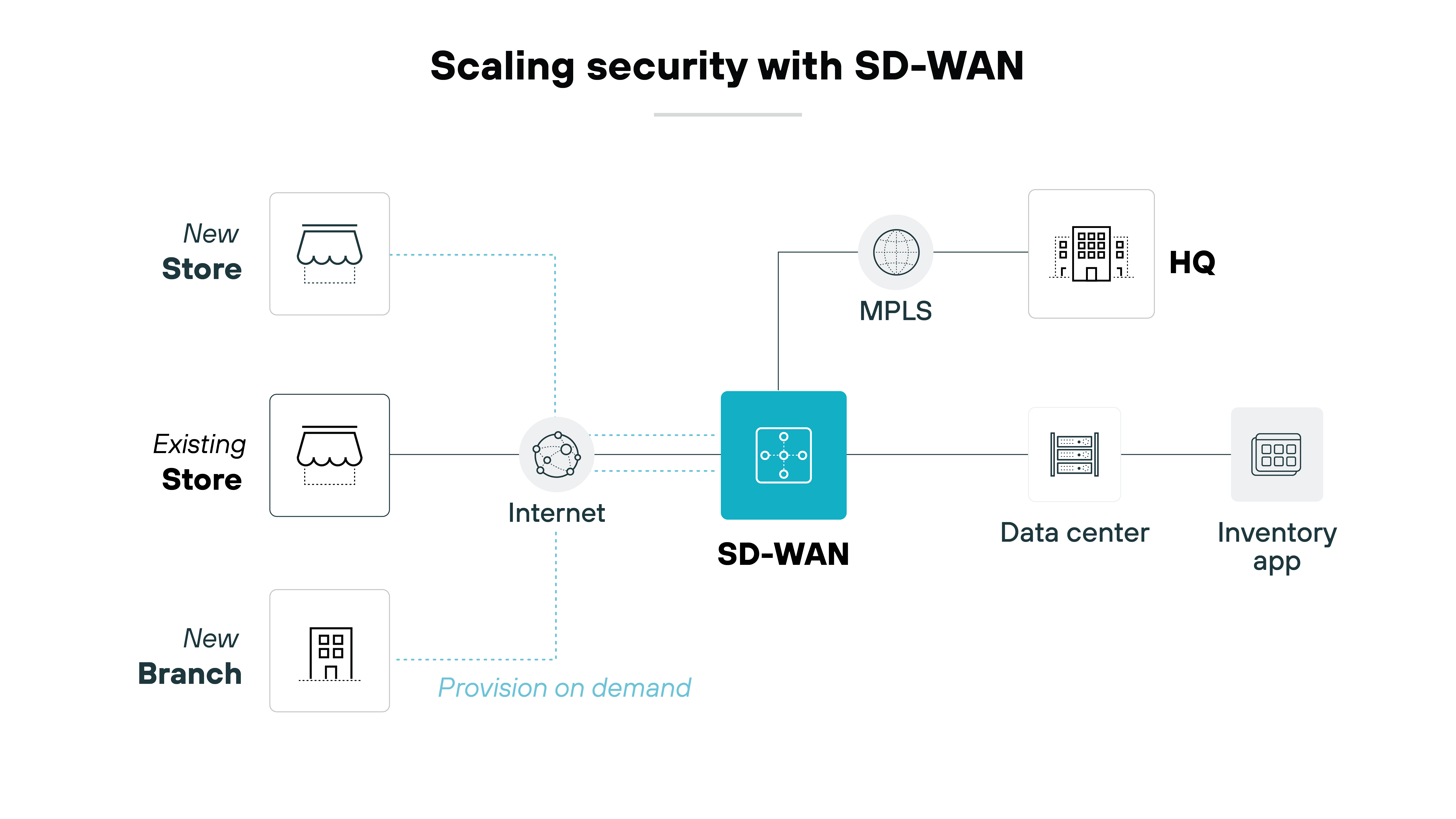
As networks expand, network security teams also have to make sure that security measures scale effectively to cover all new network segments and devices.
But the distributed nature of SD-WAN architecture requires a scalable security solution that can adapt to growing network demands without compromising security effectiveness.
Integration of advanced security features
Integrating advanced security technologies within SD-WAN overall is essential, but hard to do.
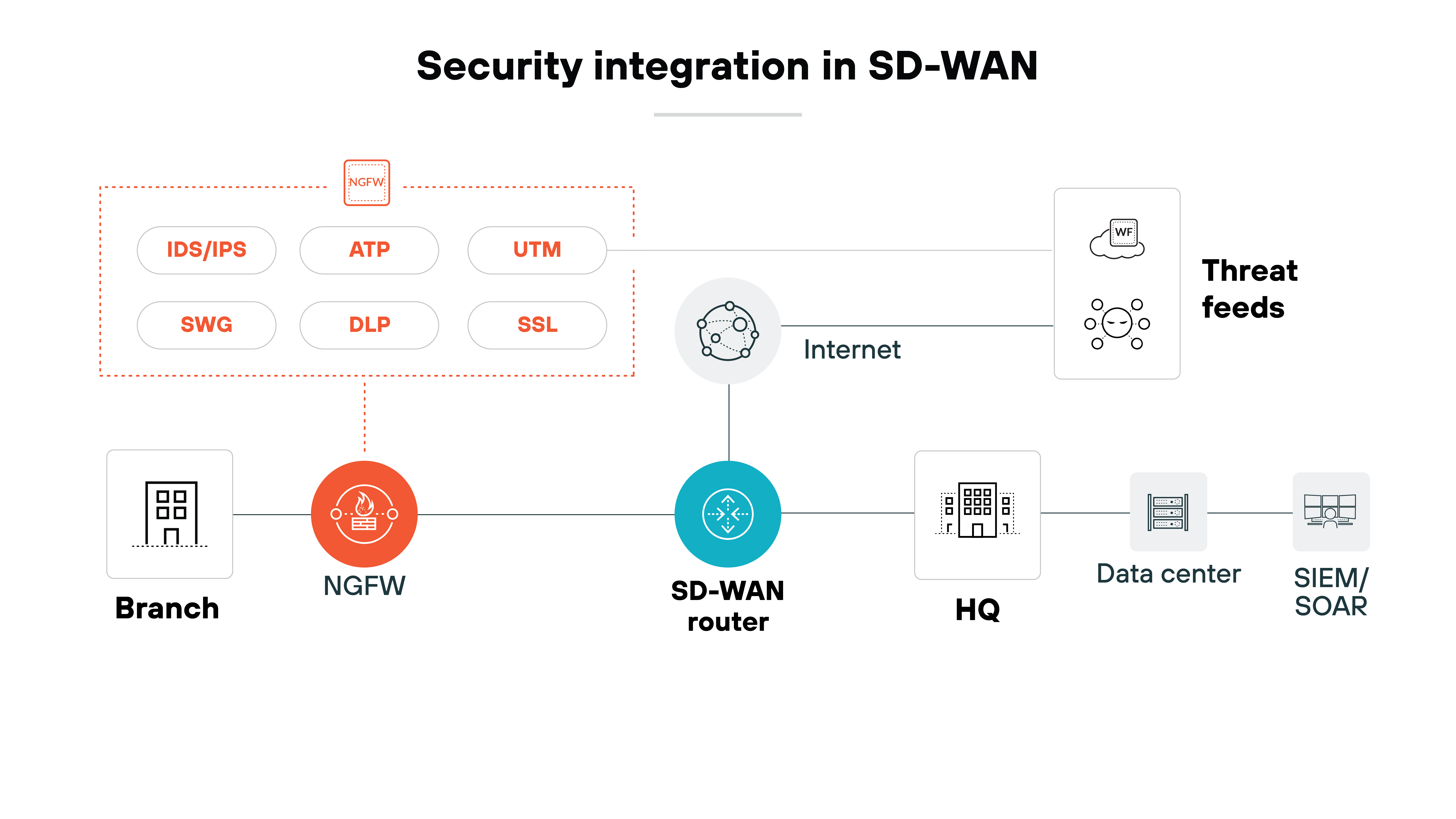
Integrating next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and advanced threat protection services with SD-WAN infrastructure is necessary for security. But the integration can be complex and requires very careful configuration to ensure compatibility and effectiveness across the network.
What are the primary SD-WAN security features?
It’s well established that as enterprises adopt cloud technologies and support more remote workforces, the traditional network perimeter has dissolved. While advancements in technology overall are aplenty, networking included, organizations are obviously facing significant security challenges as a result.
The shift in how businesses operate makes security a major priority when it comes to SD-WAN architecture—especially considering that traditional SD-WAN is not a network security solution.
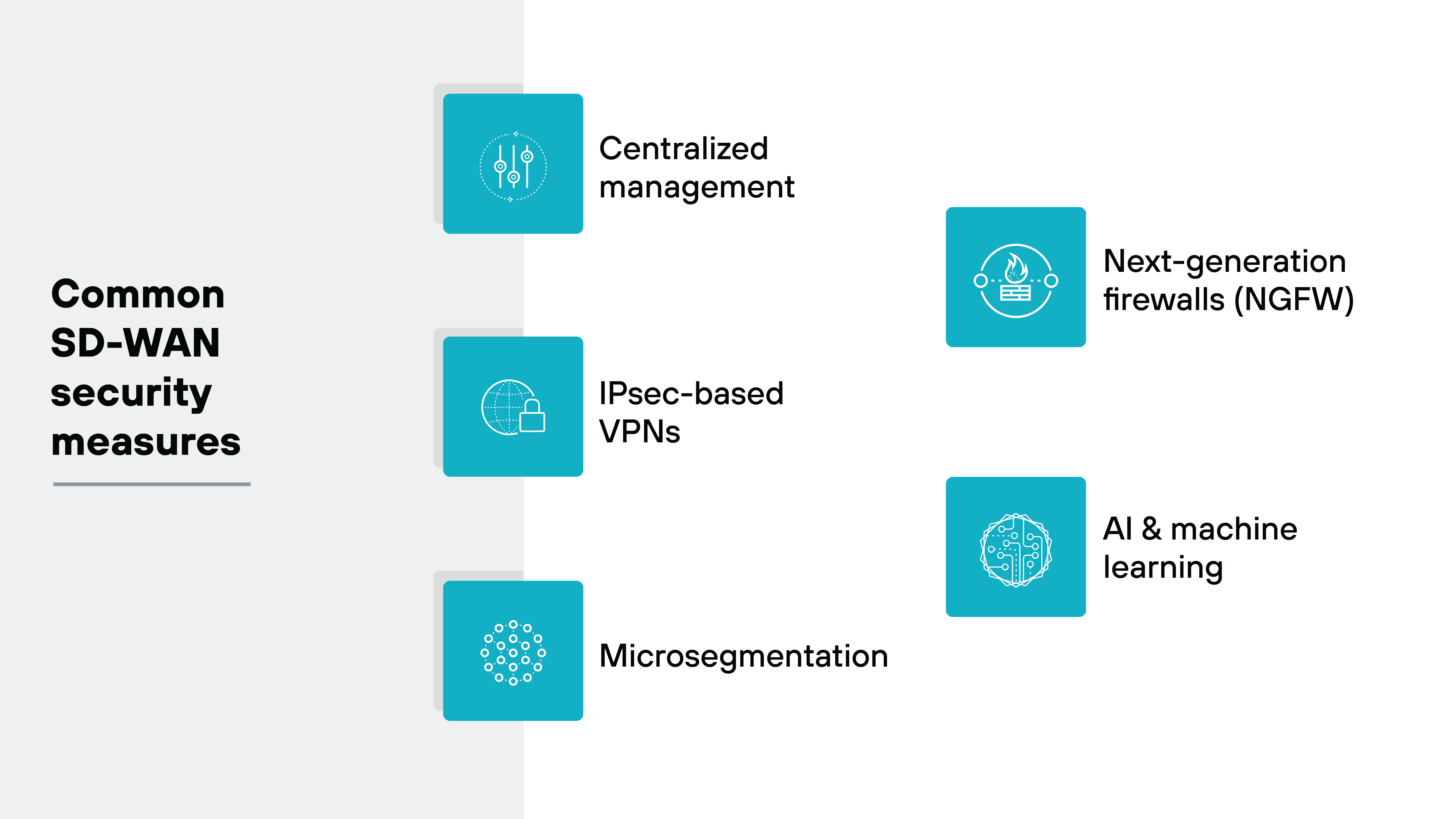
When it comes to SD-WAN security efforts, there are a number of primary measures, features, tools, and solutions you can expect to encounter, including but not limited to:
- Centralized management
- IPsec-based VPNs
- Microsegmentation
- Next-generation firewalls (NGFW)
- AI and machine learning
Let’s take a closer look at each.
Centralized management
Centralized management is a cornerstone of SD-WAN security. It streamlines the process of deploying and managing security policies across the network.
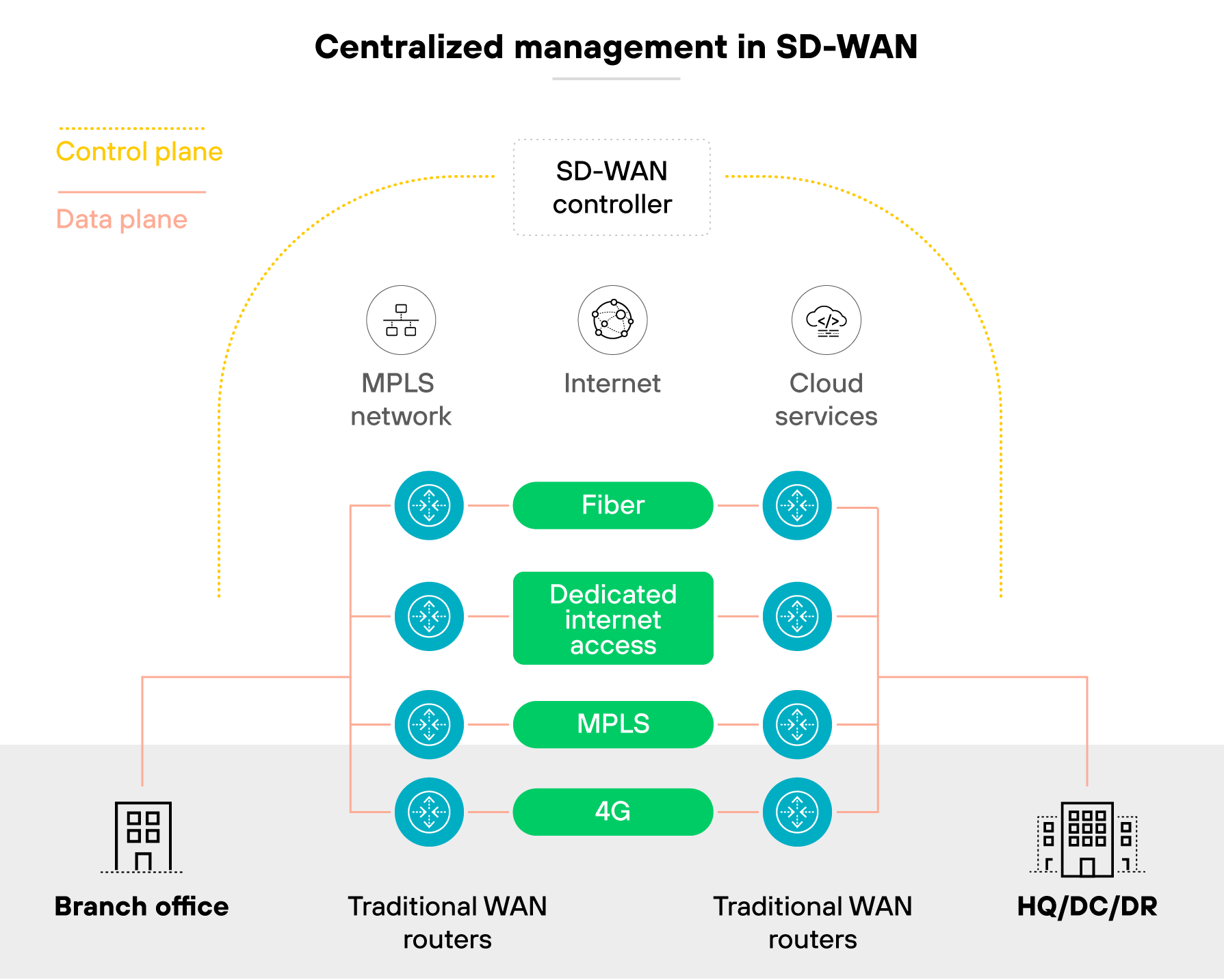
By centralizing control, businesses can create, modify, and apply security policies uniformly from a single location. This approach not only simplifies administration but also reduces the risk of configuration errors that could lead to security vulnerabilities.
IPsec-based VPNs
IP security (IPsec) is a common tactic used for protecting data transmitted over the public internet, which is a common scenario in SD-WAN setups.
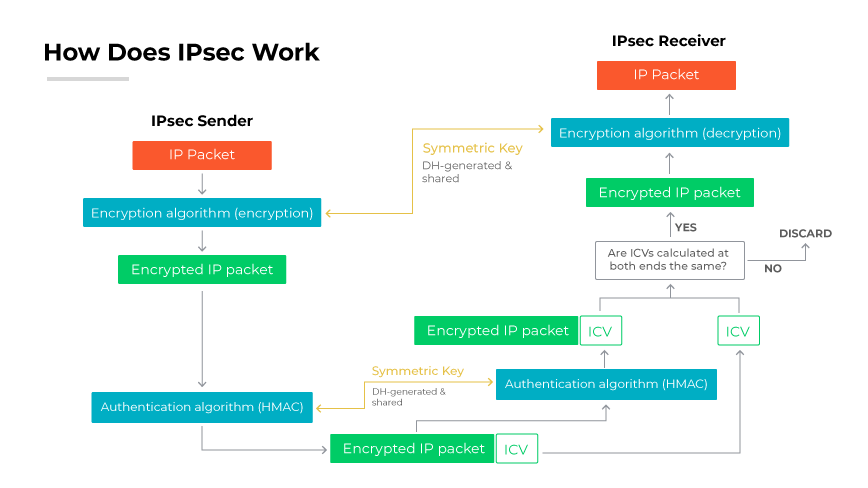
IPsec secures VPN communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session. It includes protocols like internet key exchange (IKE) for secure key management, authentication headers (AH) for data integrity, and encapsulating security payload (ESP) for encrypting data to prevent eavesdropping.
Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation is another security measure that’s helpful in the context of SD-WAN security.
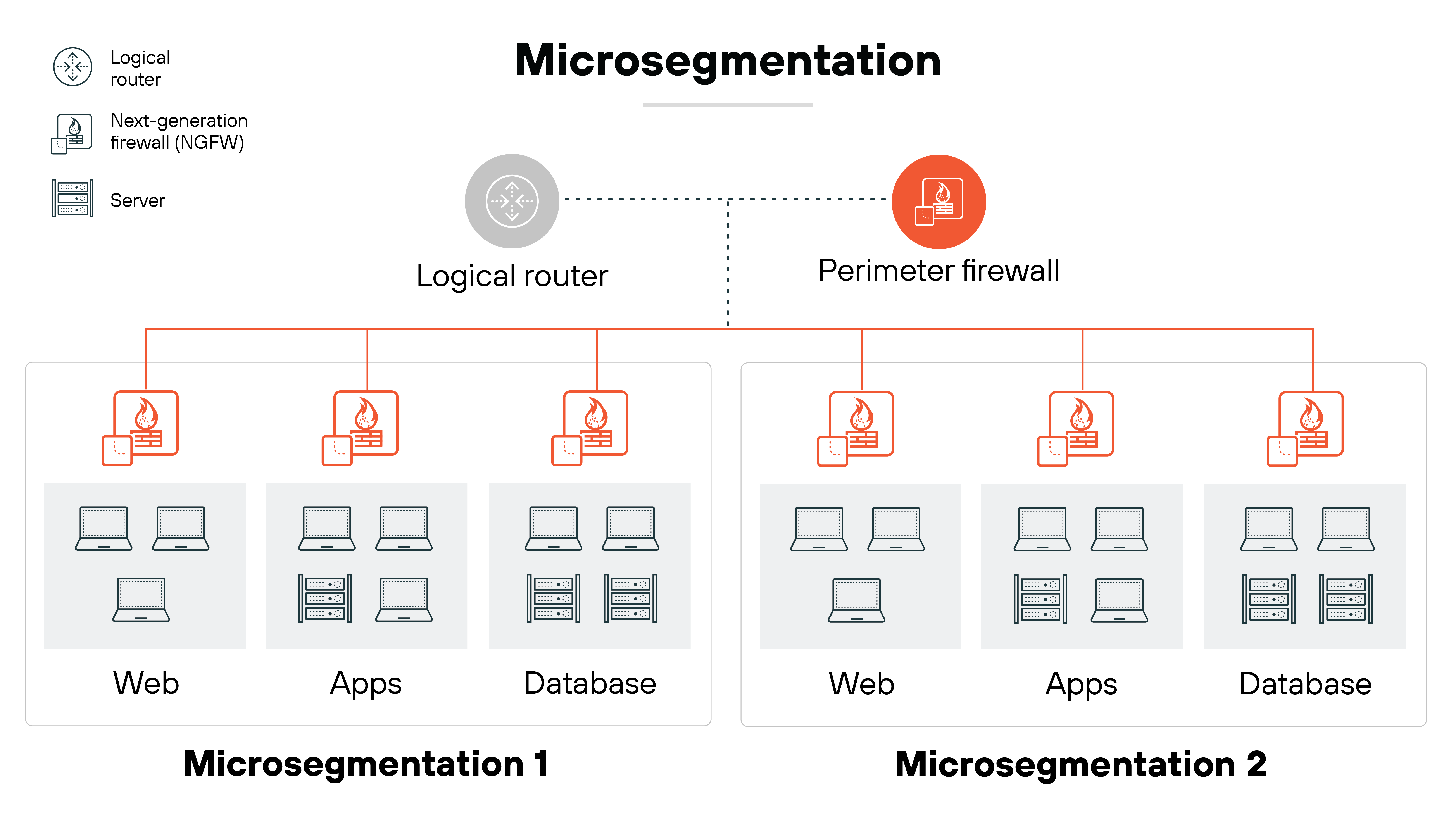
Microsegmentation allows fine-grained security controls over network traffic. It also makes it possible to secure zones in data centers and cloud environments, isolating workloads from one another and securing them individually. Which is particularly beneficial when it comes to stopping lateral movement of threats within networks and containing potential breaches.
Next-generation firewalls (NGFW)
Possibly the bread and butter of SD-WAN security features, modern NGFWs offer comprehensive network security features like application awareness, SSL inspection, intrusion prevention, deep packet inspection, and more.
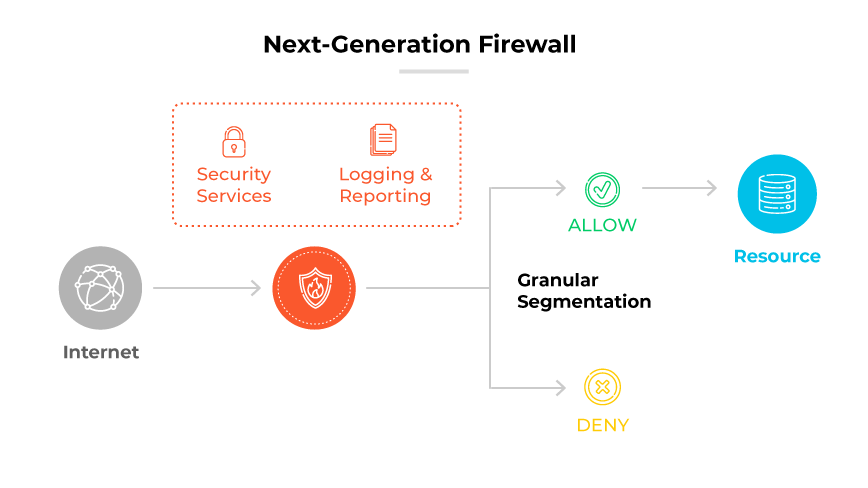
Further reading: How Are Firewalls and SD-WAN Related?
AI and machine learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are being used in SD-WAN solutions increasingly.
The objective is generally to enhance security operations. AI/ML technologies help predict, identify, and respond to anomalies and potential threats in network traffic.
By learning from network traffic patterns, AI can automate threat detection and response processes. And that reduces the time it takes to identify and mitigate security threats. It also majorly lessens the need to rely on manual intervention.
What is AI’s role in improving SD-WAN security?
As networks become more complex and dispersed, the integration of AI allows organizations to manage networks more efficiently and securely. AI's ability to learn and adapt to new threats makes it a major boon in the ongoing effort to secure SD-WAN environments against sophisticated cyber threats.
AI is dramatically transforming SD-WAN security by automating complex tasks that typically require human intervention.
Here's how:
AI enhances threat detection and response mechanisms within SD-WAN frameworks.
By analyzing vast amounts of network traffic data, AI can identify suspicious patterns and anomalies that might elude traditional monitoring tools. Taking a proactive approach means network security teams can identify and mitigate threats swiftly—usually before they impact network performance or compromise data.
For example: AI-driven systems can detect unusual data transmissions or unauthorized access attempts, triggering immediate automated responses to isolate threats and protect network integrity.
Also:
AI streamlines the management of network security policies. In dynamic business environments, network configurations can change frequently. In the past, changes traditionally required manual updates to security protocols—a process which is seriously prone to oversights and errors.
AI simplifies this by automatically adjusting security settings in response to network changes. Which means consistent protection across all nodes and pathways. This enhances security, but it also reduces administrative burden on network security teams.
AI's role extends to optimizing network performance, which indirectly boosts SD-WAN security.
By predicting traffic flows and potential bottlenecks, AI can reroute traffic to prevent overloads and minimize points of vulnerability.
This capability is extremely useful when it comes to maintaining the integrity and availability of the network. Especially during peak usage times or in the event of an attempted DDoS attack.
Further reading: Why Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Are Key Technologies for SD-WAN
What is the role of SASE in SD-WAN security?
Transitioning to secure access service edge (SASE) architecture significantly enhances SD-WAN security by integrating networking and security services through a cloud-delivered model.
While SD-WAN optimizes network performance and connectivity, SASE provides comprehensive security features that are essential in today's increasingly distributed networks.
SASE merges various security functions like secure web gateways (SWG), cloud access security brokers (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and zero trust network access (ZTNA) with SD-WAN capabilities.
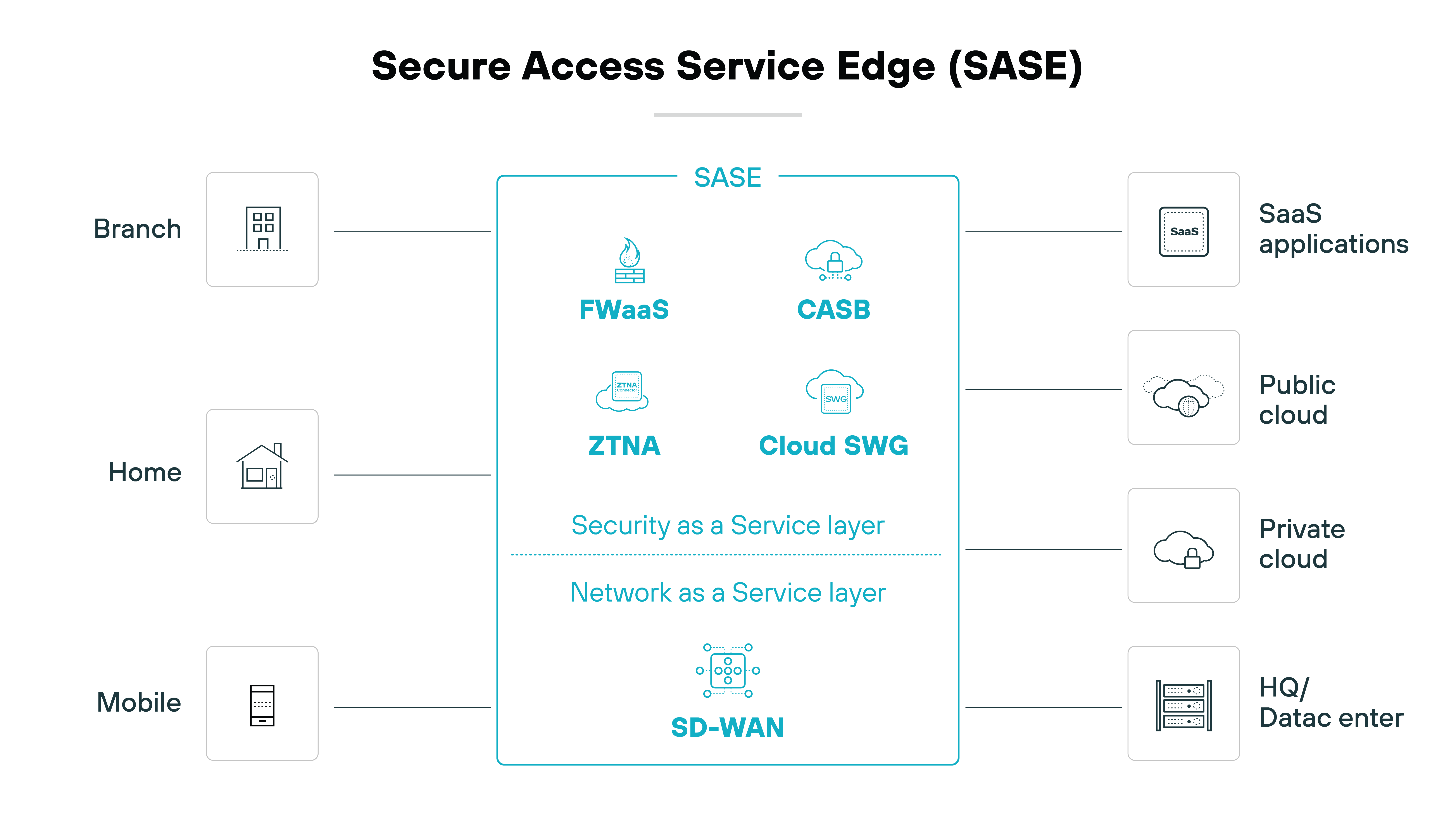
It gives organizations a unified way to securely connect all entities—remote and mobile users, branch offices, and data centers—to applications and services scattered across multiple cloud environments.
Security benefits of SASE include:
- Enhanced security at the edge
SASE shifts the focus of security from the traditional data center-based perimeter to a more dynamic, edge-oriented approach.
By moving security functions closer to the point of access, SASE reduces latency, enhances performance, and improves the security of access regardless of location. This is especially beneficial for remote workers or branches accessing cloud-based resources—where traditional network architectures might expose the organization to increased risks.
- Simplified management and reduced complexity
With SASE, organizations can manage both networking and security policies from a single pane of glass.
The integrated approach makes administration way easier. It also ensures that security policies are consistently enforced across all locations and endpoints.
SASE eliminates the complexities associated with managing multiple standalone security products, which often operate in silos and can lead to gaps in security coverage—a common SD-WAN security issue.
- Adaptive security posture
The cloud-native architecture of SASE allows it to seamlessly scale and adapt to the evolving needs of the business.
Security policies and protections can be dynamically adjusted based on real-time traffic analysis, user behavior, and threat intelligence.
The adaptive security posture is crucial for dealing with advanced threats and ensuring compliance across diverse regulatory environments.
- Cost-effectiveness
By consolidating multiple security functions into a single framework, SASE can reduce the overall cost of ownership associated with purchasing, integrating, and maintaining various discrete security appliances and software.
Additionally, the cloud-based nature of SASE reduces the need for on-premises hardware, which further lowers capital expenditures and operational costs.
Further reading:
Do next-generation SD-WAN solutions provide better security?
Yes, next-generation SD-WAN solutions provide better security than traditional SD-WAN solutions.
As established, while businesses rapidly evolve with more applications and services moving to the cloud, traditional network architectures struggle to keep up—especially when it comes to security.
Traditional SD-WANs do improve connectivity costs and flexibility, but they also majorly lack robust security features. Which makes additional security appliances or services necessary. Again, that can complicate network management and escalate costs.
However:
Next-generation SD-WAN integrates advanced security features directly into the network fabric. It provides centralized policy management and real-time threat intelligence. And next-gen SD-WAN solutions rely on cloud connectivity to extend security to every endpoint, regardless of location.
These systems are not just about connecting sites; they're about securing those connections dynamically. Integrated security within SD-WAN means that encryption, intrusion prevention, and content filtering are handled centrally and uniformly, ensuring consistent enforcement across the network.
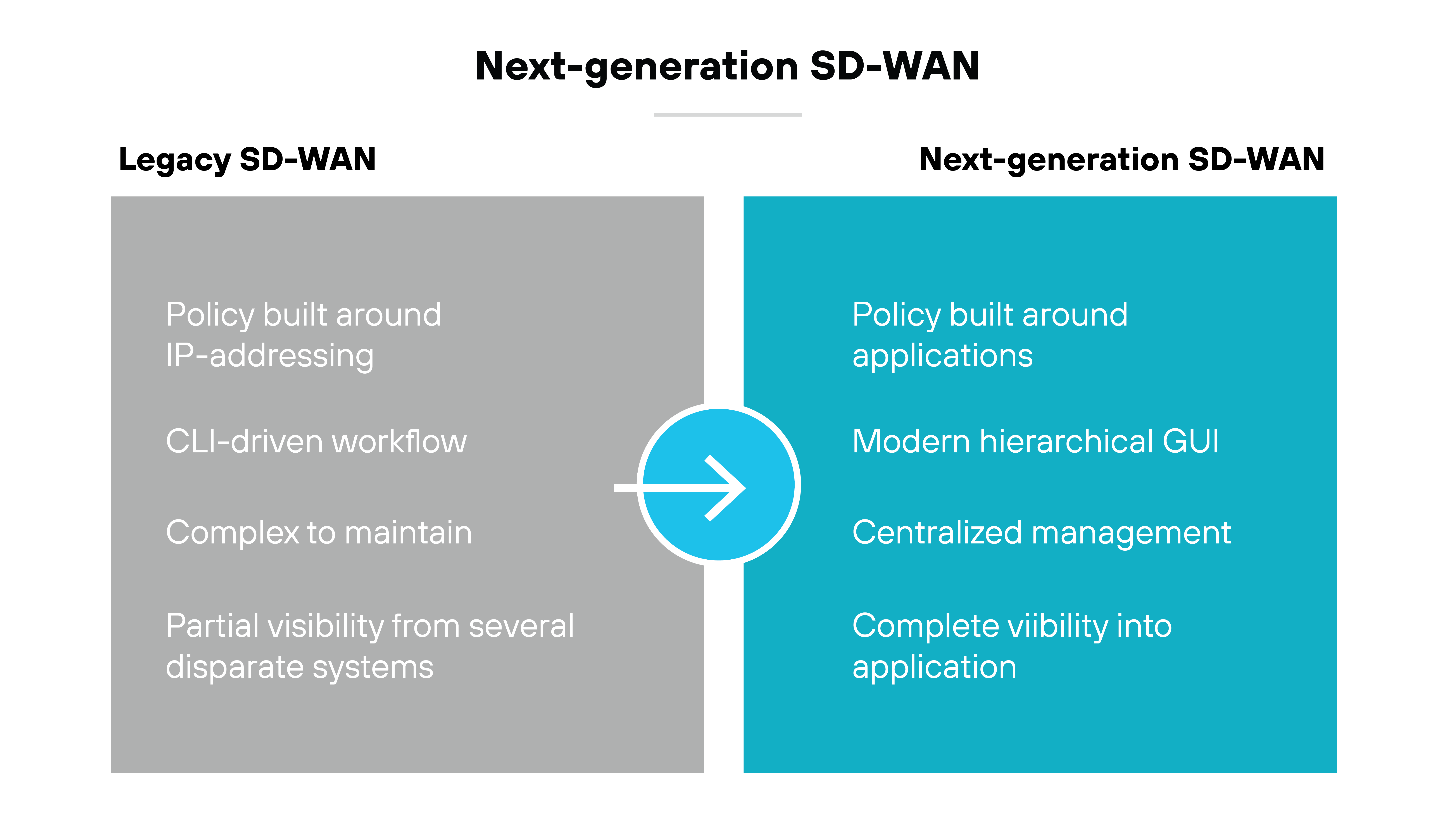
Here’s why this matters:
This approach significantly simplifies security management and reduces the likelihood of configuration errors that could lead to vulnerabilities.
Also, with the ability to segment network traffic, next-gen SD-WAN can isolate sensitive data and restrict access to compromised systems. And that limits the spread of potential attacks.
Plus: Next-gen SD-WAN solutions use AI and ML to predict and respond to network anomalies in real-time. And taking a proactive stance on network threats means organizations can prevent disruptions instead of just reacting to them.
Which means that organizations can achieve a much higher level of security that is both adaptive to their needs and easier to manage.
Further reading: What Is Next-Generation SD-WAN?
What is the difference between SD-WAN security and secure SD-WAN?
"Secure SD-WAN" and "SD-WAN security" are terms that often appear together but represent distinct concepts within the domain of network management.
Both terms involve the security of SD-WAN networks. Basically, SD-WAN security is more about the application of various security strategies to protect the network, while secure SD-WAN is inherently security-focused with integrated solutions.
More specifically:
SD-WAN security pertains to the security measures and protocols implemented to protect the integrity and data of an SD-WAN network. It’s not necessarily an industry standard term, so it can mean slightly different things to different people. However, fundamentally, SD-WAN security involves integrating additional security services or devices to enhance the security of an existing SD-WAN setup.
Secure SD-WAN refers specifically to SD-WAN solutions that are designed with integrated security features from the outset. Again, this design philosophy ensures security is not an afterthought but a fundamental component of the network architecture.
Further reading: What Is Secure SD-WAN? | What It Is and How It Works
SD-WAN security FAQs
The biggest security risk with SD-WAN is increased vulnerabilities due to direct internet access at branch locations, which exposes network traffic to potential threats and breaches without traditional centralized security controls.
WAN security involves applying protective measures and protocols to safeguard the integrity and data of a Wide Area Network (WAN), including the use of firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to defend against external threats and vulnerabilities.
No, SD-WAN is not the same as a firewall. SD-WAN is a networking technology that enhances connectivity and control across wide area networks using software-defined networking principles, while a firewall is a security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
SD-WAN enhances security by integrating advanced security features such as next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and encryption protocols like IPsec. It also allows for centralized management of security policies and microsegmentation to isolate and protect network segments.

