- 1. How are we defining 'hardware' and 'software' firewalls in this article?
- 2. What decision are you really making when it comes to hardware vs. software firewalls?
- 3. How does network placement differ?
- 4. Which use cases apply to one type of firewall over the other?
- 5. What are the key performance dimensions to compare?
- 6. How do scaling and failover work in each model?
- 7. How are policies, updates, and drift managed?
- 8. What are the cost and licensing trade-offs to expect?
- 9. Can you (and should you) run both?
- 10. How to decide between hardware and software firewalls
- 11. Hardware vs. software firewalls FAQs
- How are we defining 'hardware' and 'software' firewalls in this article?
- What decision are you really making when it comes to hardware vs. software firewalls?
- How does network placement differ?
- Which use cases apply to one type of firewall over the other?
- What are the key performance dimensions to compare?
- How do scaling and failover work in each model?
- How are policies, updates, and drift managed?
- What are the cost and licensing trade-offs to expect?
- Can you (and should you) run both?
- How to decide between hardware and software firewalls
- Hardware vs. software firewalls FAQs
Hardware Firewalls vs. Software Firewalls: A Comparison
- How are we defining 'hardware' and 'software' firewalls in this article?
- What decision are you really making when it comes to hardware vs. software firewalls?
- How does network placement differ?
- Which use cases apply to one type of firewall over the other?
- What are the key performance dimensions to compare?
- How do scaling and failover work in each model?
- How are policies, updates, and drift managed?
- What are the cost and licensing trade-offs to expect?
- Can you (and should you) run both?
- How to decide between hardware and software firewalls
- Hardware vs. software firewalls FAQs
The difference between hardware and software firewalls is that hardware firewalls are delivered as dedicated appliances while software firewalls are deployed as virtual instances.
A hardware firewall uses purpose-built processors and interfaces to enforce security at physical network boundaries. A software firewall runs on general-purpose compute in cloud or virtual environments to protect workloads and east–west traffic.
How are we defining 'hardware' and 'software' firewalls in this article?
A hardware firewall is a dedicated appliance. It has its own processors, memory, and interfaces built solely for inspecting and controlling traffic. The device sits physically between networks and enforces policies as packets flow through its ports.
A software firewall delivers the same functions but in a virtualized form factor. It runs as a process on a server, a virtual machine, or a cloud instance. It can also be packaged for container platforms. In other words, the firewall logic is delivered as software instead of a stand-alone device.
Both enforce traffic inspection, policy application, and logging. The difference lies in how they are deployed and operated.
By narrowing the definition to these two form factors, we can make an apples-to-apples comparison. That way, the focus stays on how dedicated appliances and software instances each serve as network enforcement points.
- What Is a Virtual Firewall?
- What Is a Container Firewall?
- What Is Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)? | FWaaS Defined & Explained
What decision are you really making when it comes to hardware vs. software firewalls?
The distinction isn't about which type of firewall is better. It's about where the enforcement point sits and how you expect to manage it.
A hardware firewall anchors traffic control at a physical boundary. A software firewall places the same enforcement inside virtual or cloud environments.
Which means: The decision is situational. Some networks need predictable, appliance-based performance. Others need the agility to spin up enforcement wherever workloads run.
Many organizations use both. The choice comes down to aligning form factor with traffic placement and your operational model.
How does network placement differ?
Network placement is one of the clearest ways hardware and software firewalls diverge. Some enforce policies at physical boundaries. Others sit inside virtual or cloud environments.
Let's dig into the different placements to see where each form factor fits best.
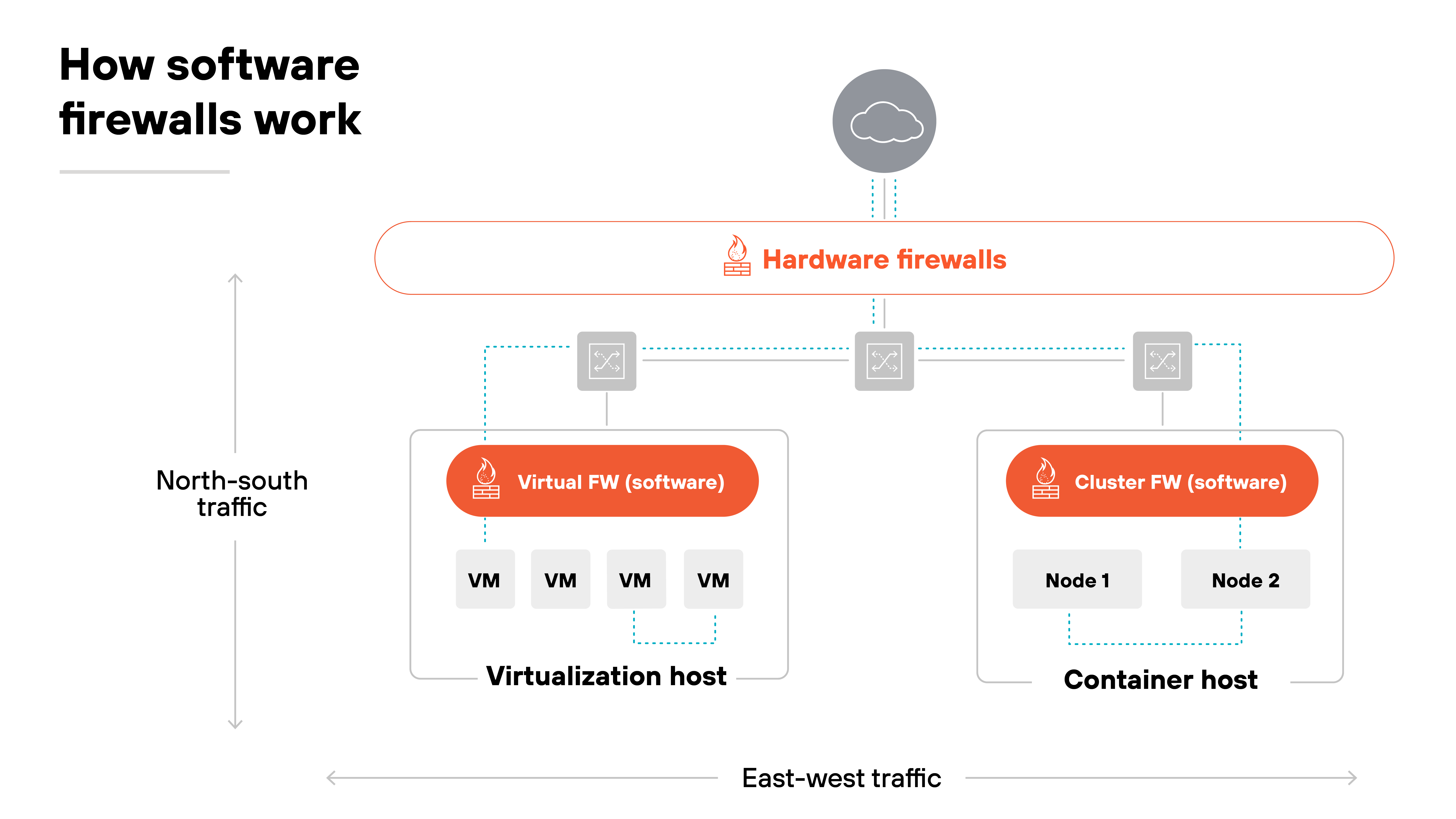
- North–south traffic: This is the first axis to consider. North-south traffic moves in and out of a network. Hardware firewalls are often placed at these edges—such as the internet perimeter of a data center or the edge of a campus network.
- Branch offices: Branches are another placement. Here, hardware appliances may still serve as enforcement points. But software firewalls can also run on existing servers or white-box hardware to reduce footprint.
- Data center cores: Commonly anchored with hardware appliances. The reason is predictable performance. Physical firewalls handle high throughput between aggregation layers without sharing resources with other workloads.
- Cloud environments: The cloud shifts enforcement inside virtual edges. Software firewalls can be deployed at VPC or VNet boundaries to monitor both inbound and outbound flows.
- East–west traffic: East-west traffic tells a different story. This is communication between workloads, not just in and out. Software firewalls secure VM-to-VM traffic within virtualized data centers. They also protect container traffic by integrating with orchestration platforms like Kubernetes
The takeaway: Placement depends on where the traffic flows. Hardware aligns with physical edges and core aggregation. Software aligns with virtual boundaries and distributed workloads.
Which use cases apply to one type of firewall over the other?
Use cases make the differences more tangible. They highlight the environments where hardware or software firewalls align best with operational needs.
The table below summarizes common scenarios and which model they align with. Each example is then explained in more detail.
| Hardware vs. software firewall use cases by form factor |
|---|
| Use case | Applies to |
|---|---|
| Branch offices | Software (though hardware may still be used for larger or critical branches) |
| Public cloud | Software |
| Inter-VPC or inter-VNet traffic | Software |
| Microsegmentation (VM-to-VM, containers) | Software |
| Operational technology and industrial networks | Hardware |
| Pop-up or temporary sites | Both, depending on available resources |
| Compliance-bound or air-gapped environments | Hardware |
Branch offices
Smaller branches may not have space or staff for appliances. A software firewall can run on existing servers or white-box hardware.
Applies to: Software (though hardware can still be used for larger or critical branches).
Public cloud
Physical appliances can't be placed inside a cloud provider's infrastructure. Software firewalls extend inspection and policy enforcement to VPCs and VNets.
Applies to: Software.
Inter-VPC or inter-VNet traffic
East–west traffic between cloud environments needs segmentation. Software firewalls integrate with cloud routing to enforce those controls.
Applies to: Software.
Microsegmentation
VM-to-VM and container traffic require fine-grained control. Software firewalls support segmentation at the workload and service level.
Applies to: Software.
Operational technology and industrial networks
Environments with rugged hardware requirements often need tamper-resistant devices. Hardware firewalls meet physical and compliance constraints.
Applies to: Hardware.
Pop-up or temporary sites
Some sites lack permanent infrastructure. A small hardware appliance can be deployed quickly. If infrastructure already exists, software may be simpler.
Applies to: Both, depending on available resources.
Compliance-bound or air-gapped environments
Some regulated environments require certified, physically controlled devices. Hardware firewalls meet those requirements more directly.
Applies to: Hardware.
What are the key performance dimensions to compare?
Performance isn't about feature sets. It's about how each form factor holds up under load.
The three dimensions that matter most are:
- Throughput
- Session capacity
- TLS decryption
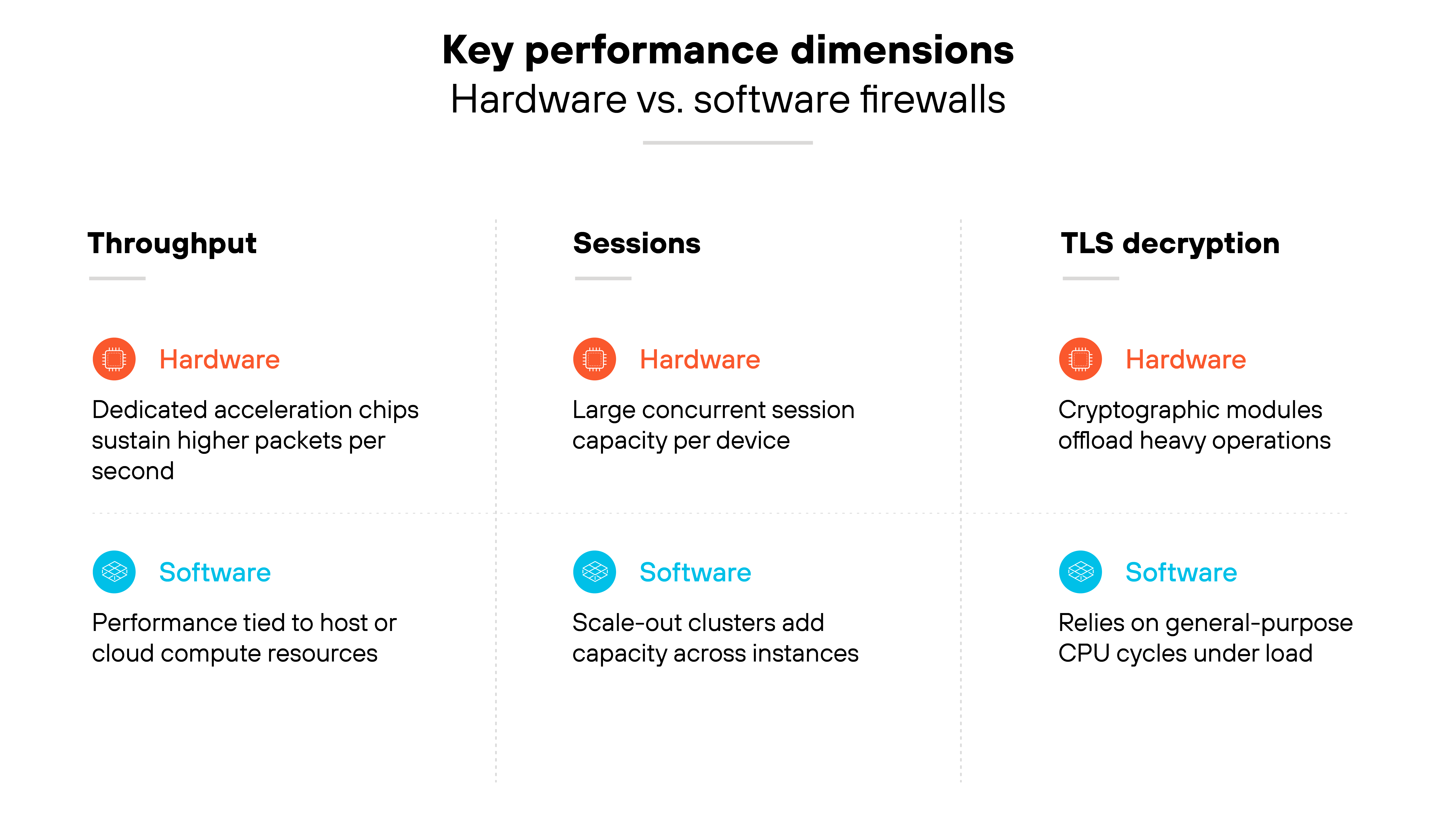
Throughput
Throughput is the raw volume of traffic a firewall can handle. Hardware appliances often include acceleration chips to sustain higher packets per second (PPS). Software firewalls rely on shared compute, so throughput is tied to the capacity of the host server or cloud instance.
Session capacity
Session capacity is the number of concurrent connections the firewall can track. Hardware devices support large numbers of sessions with dedicated memory and processors. Software firewalls may support fewer sessions per instance. On the other hand, they can scale horizontally, adding instances when demand grows.
TLS decryption
TLS decryption is often the most resource-intensive task. Hardware firewalls may use cryptographic acceleration modules to maintain performance. Software firewalls consume general-purpose CPU cycles, so heavy encryption can theoretically reduce efficiency if it's not paired with an external decryption card.
Important: These aren't weaknesses of either form factor. They're just design characteristics. The results depend on how much traffic, how many sessions, and how much encrypted data your network carries.
So what should you measure across both?
Peak and average traffic rates. Packet size distribution. The percentage of encrypted sessions. These metrics will give you a realistic view of how either option performs in your environment.
How do scaling and failover work in each model?
Scaling and resilience are handled differently in hardware and software firewalls. The focus here is on how capacity grows and how continuity is maintained if something fails.
Hardware firewalls are usually deployed in high-availability pairs or clusters.
State information is synchronized so if one unit fails, the other takes over with minimal disruption. Some appliances also include fail-to-wire or bypass options, allowing traffic to continue flowing even if the device itself stops inspecting packets.
Why is this important?
Because hardware capacity is tied to the appliance. Growth often means adding another pair or upgrading to a larger model. That gives predictable performance but fixed expansion steps.
On the other hand, software firewalls scale by adding more instances.
In cloud environments, they can be grouped in scale-out clusters or managed by autoscaling policies. This means additional capacity can be provisioned quickly through orchestration tools.
Failover also works differently. Software firewalls can be configured for zone-aware resilience, shifting traffic to healthy nodes if one instance becomes unavailable. Provisioning is often faster because it relies on automation rather than manual replacement of equipment.
Remember: Neither approach is inherently superior. They simply reflect the design of each form factor.
Hardware emphasizes reliability through clustering and physical redundancy. Software emphasizes elasticity and rapid recovery through automation.
Choose the model that aligns with how your environment grows and how you need traffic to stay protected during failures. In many cases, you'll need both.
How are policies, updates, and drift managed?
Managing firewalls is not only about inspection. It's also about keeping policies consistent, applying updates, and preventing drift.
Hardware firewalls are maintained at the appliance level. Updates are staged and committed directly to the device.
Lifecycle refreshes are expected, since each unit eventually needs replacement or hardware support renewals. Basically, management is tied to each appliance and its refresh cycle.
Software firewalls shift this model. Policies are often defined in centralized templates.
They can be distributed across many instances through automation. Infrastructure-as-code tools and APIs make it possible to integrate firewall policies into broader deployment workflows. This means updates and rollbacks can be handled programmatically instead of manually.
Why does drift matter?
Because both models can lose alignment over time.
Hardware devices may diverge if changes are made locally instead of through a management system. Software instances may drift if templates are not enforced consistently across environments.
It's important to note: Drift could be a potential challenge in either form factor.
Consistency depends less on form factor than on how policies are managed and enforced. And that's largely dependent upon whether the firewall vendor offers a centralized management plane for both form factors.
What are the cost and licensing trade-offs to expect?
| Hardware vs. software firewall cost models |
|---|
| Cost dimension | Hardware firewall | Software firewall |
|---|---|---|
| Primary model | CapEx: appliance purchase, refresh cycles, bundled licensing | OpEx: cloud instance fees, elastic scaling, per-vCPU or per-instance licensing |
| Cost predictability | Predictable, tied to device lifecycle and support contracts | Variable, tied to workload demands and cloud usage |
| Secondary costs | Shipping, installation, lifecycle management | Cloud egress fees, licensing complexity across regions or instances |
Costs show up differently depending on the form factor.
Hardware firewalls are usually a capital expense.
You purchase the appliance, renew support contracts, and eventually budget for refresh cycles. Licensing often comes bundled with features or throughput tiers, which means ongoing commitments alongside the physical device.
That said, the industry is steadily moving toward subscription models for both hardware and software. So cost structures are converging even if the form factors differ.
Software firewalls move those costs into operating expenses.
You pay for cloud instances or VM resources, plus the software license. Scaling is elastic. Which means: More traffic or workloads can be covered by spinning up more instances. But every instance adds cost, so charges can grow quickly if usage spikes.
Secondary costs matter too. For hardware, shipping, installation, and lifecycle management all add up.
For software, cloud egress fees and licensing complexity can surprise teams. For instance, outbound traffic across regions may cost more than anticipated, and licensing may tie to per-vCPU or per-instance metrics that are hard to forecast.
On the other hand, software's pay-as-you-go model can be efficient for variable workloads.
Hardware can be more predictable when traffic patterns are stable.
The key is to align pricing models with your environment. If you value long-term stability, appliances may be easier to budget. If elasticity matters, software may fit better.
Can you (and should you) run both?
Yes — many organizations do. The reason is simple. Hardware and software firewalls complement each other.
Hardware appliances anchor the network edge.
They provide predictable enforcement where traffic enters or leaves a data center, branch, or campus. These devices are purpose-built to handle large volumes and sustain performance.
Software firewalls fill the gaps hardware cannot reach.
They sit inside cloud environments, between virtual machines, or at container layers. So they can enforce policies closer to workloads and support east–west segmentation.
Why run both?
Because traffic flows are no longer confined to one perimeter. A hybrid approach ensures you can cover physical boundaries and distributed workloads with the same policy logic.
However: This can also create management challenges. Different form factors mean multiple enforcement points. Without centralized control, policies can drift or become inconsistent.
Fortunately, there's a practical solution. Which is unified management. Central consoles, APIs, or orchestration tools can align policies across appliances and software instances. This reduces the risk of blind spots while keeping operations consistent.
Running both hardware and software firewalls is not only possible but often necessary. The key is to approach it as a hybrid model with coordinated management. Not as two disconnected strategies.
How to decide between hardware and software firewalls
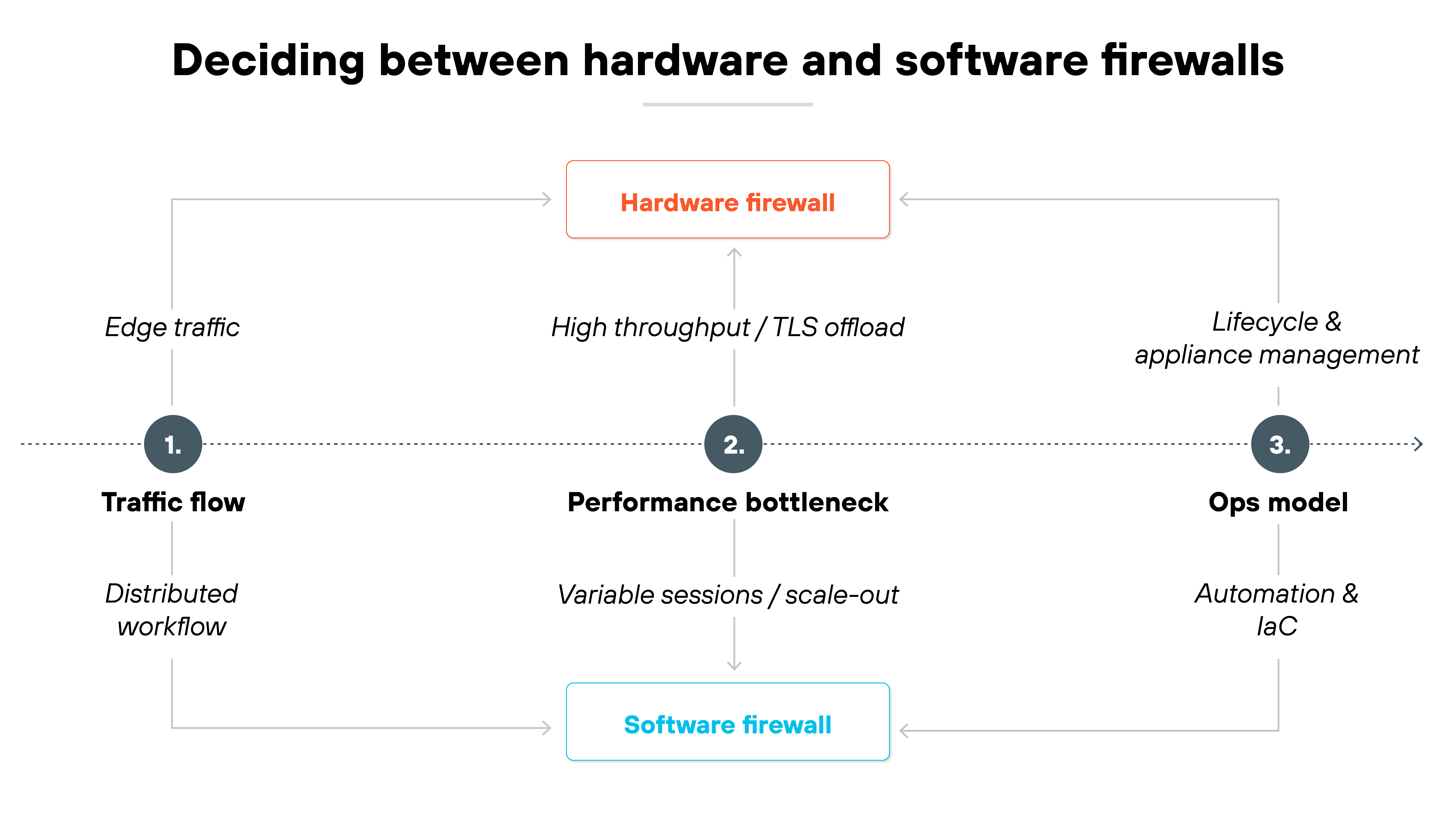
Deciding between the two isn't about features because hardware and software firewalls do the same things. It's about aligning the form factor with how your network actually operates.
A quick way to think about it is to ask three questions.
-
Where does your traffic flow?
- If most of it still passes through a clear edge, a hardware firewall may fit best.
- If workloads are spread across cloud or virtual environments, software may align better.
-
What bottlenecks first in your environment?
Throughput, session count, or TLS decryption capacity.
- Hardware devices often maintain higher throughput with dedicated acceleration.
- Software can scale out, but each instance may support fewer sessions or handle TLS less efficiently.
-
How do you plan to operate it?
- If your team is built for appliance lifecycle management, hardware may be easier to maintain.
- If you rely on automation and infrastructure-as-code, software integrates more naturally.
The decision is situational. Some networks lean heavily one way. Many end up blending both. The key is to let traffic patterns, performance constraints, and operational models guide the choice instead of treating it as a binary either-or.